72% of security breaches happen because of code vulnerabilities? (Source: PT Security) That’s a staggering number, and yet, many organizations still push code into production without proper security checks.
By integrating automated code scanning into MuleSoft CI/CD pipelines, you can catch security flaws early, ensure compliance, and release higher-quality software—without slowing down development.
In this blog, we’ll cover:
- The best tools for scanning MuleSoft code
- How to seamlessly integrate security into your CI/CD pipeline
- Best practices to stay compliant and secure
Why CI/CD is Critical in Modern DevOps
In today’s fast-paced development world, releasing software quickly and securely is non-negotiable. Traditional deployment methods—filled with manual approvals, code conflicts, and last-minute bugs—simply can’t keep up.
This is where Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) comes in.
The CI/CD Difference
| Process | Manual Deployment | CI/CD Pipeline |
| Deployment Time | Hours to Days | Minutes |
| Error Rate | High | Low (automated testing) |
| Rollback Capability | Slow and Risky | Instant and Controlled |
| Scalability | Limited | Seamless |
Key Benefits of CI/CD in Enterprises
- Faster Releases – Automate everything from builds to deployments.
- Stronger Security – Detect vulnerabilities early with integrated code scanning.
- Better Consistency – Eliminate human errors and ensure stable releases.
- Instant Rollbacks – Quickly revert to a previous version if needed.
CI/CD isn’t just about speed—it’s about delivering secure, reliable software at scale. Let’s explore how code scanning fits into this equation!
The Case for Code Scanning: Ensuring Code Quality, Security, and Regulatory Compliance
Every software release is a potential security risk if vulnerabilities go unchecked. In MuleSoft environments, unvalidated input, misconfigured APIs, and insecure dependencies can create serious security flaws.
Is Your Code Secure?
Ask yourself these three critical questions:
- Do you regularly scan for vulnerabilities?
APIs and integrations evolve rapidly—without automated scanning, old vulnerabilities persist. - Are you meeting compliance requirements?
Regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI-DSS mandate strong security measures. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines and legal trouble. - Do you have automated security gates in your CI/CD pipeline?
If vulnerabilities slip past development, they could go live in production, putting data, users, and business operations at risk.
How a Healthcare Company Prevented a HIPAA Violation
A leading healthcare provider relied on MuleSoft to integrate patient records across multiple systems. However, a security audit revealed that sensitive patient data was exposed due to poor API security configurations.
The Solution:
- They implemented automated code scanning in their CI/CD pipeline, using Falcon Scan Maven Plugin.
- The scans immediately flagged unsecured API endpoints, preventing a major HIPAA violation.
- With automated security checks, their compliance risks dropped by 90%, ensuring patient data remained protected.
Bottom Line: Code scanning isn’t optional—it’s a necessary defense against breaches, compliance failures, and business risks. Next, let’s explore the top tools for integrating code scanning into your MuleSoft CI/CD pipeline.
Understanding Automated Code Scanning in MuleSoft Projects
As businesses embrace MuleSoft for API-led connectivity, security and compliance become critical. Code vulnerabilities can expose sensitive data, break integrations, and even lead to costly regulatory fines.
This is where automated code scanning in CI/CD pipelines comes in—proactively detecting issues before they impact production.
Let’s break down how automated scanning works, why it’s essential, and how it ensures compliance with key regulations like HIPAA and SOC 2.
What is Automated Code Scanning in CI/CD?
Automated code scanning is the process of analyzing MuleSoft code as it moves through the CI/CD pipeline. The goal is to identify vulnerabilities, enforce best practices, and ensure compliance—without slowing down development.
How It Works
- A developer commits code to a repository (e.g., GitHub, GitLab).
- A developer commits code to a repository (e.g., GitHub, GitLab).
- If vulnerabilities are detected, the pipeline can:
- Block the CICD builds ensuring non compliant code is not deployed.
- Developers can fix issues using suggestions or auto-fix.
- Only code compliant with organizational standards will be deployed.
Manual vs. Automated Code Scanning in MuleSoft
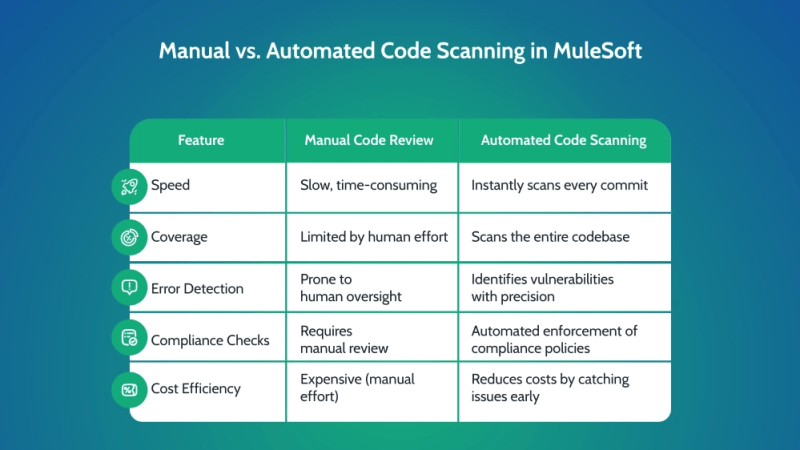
Example Scenario: How Code Scanning Prevents Security Flaws
- A developer commits API code without proper authentication done.
- The code scanning tool detects that there is no valid authentication mode implemented (e.g., no OAuth 2.0).
- The CI/CD pipeline flags the issue, preventing deployment.
- The developer updates the code with required authentication mode based on the suggestion.
- The fix is verified, and the deployment proceeds without security risks.
This proactive approach saves time, prevents vulnerabilities, and ensures secure deployments in MuleSoft environments.
Related Read – Automating MuleSoft Code Scanning: Reducing Manual Effort and Improving Code Quality
Benefits of Code Scanning for MuleSoft Integration Projects
Automated code scanning delivers four key benefits:
- Enhanced Efficiency:
- Detects vulnerabilities in seconds rather than days.
- Reduces manual review efforts, allowing developers to focus on innovation.
- Stronger Security:
- Identifies API misconfigurations, weak authentication, and potential exploits.
- Prevents data leaks and breaches before they occur.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Enforces security policies required by HIPAA, SOC 2, PCI-DSS, and GDPR.
- Ensures that APIs follow industry best practices.
- Cost Savings:
- Fixing security flaws before deployment is 10x cheaper than after release.
- Reduces downtime and reputation damage from API security failures.
Types of Code Scanning: Static Analysis, Dynamic Testing, and Security Scans
Different code scanning methods serve different security needs in MuleSoft projects.
Comparison Table: Static vs. Dynamic vs. Security Scanning
| Type of Scan | What It Does | Best Use Case in MuleSoft |
| Static Analysis | Scans source code before execution | Detects API misconfigurations, syntax errors, and best practice violations |
| Dynamic Testing | Tests running code in a staging environment | Identifies runtime vulnerabilities like insecure data transmissions |
| Security Scans | Focuses on security-specific weaknesses | Finds authentication flaws, encryption issues, and injection risks |
When to Use Each Method
- Static Analysis → Before code is committed (early-stage detection)
- Dynamic Testing → Before deploying APIs into production (real-world testing)
- Security Scans → Throughout the entire CI/CD pipeline (compliance enforcement)
By combining all three scanning methods, businesses can achieve full security coverage in MuleSoft projects.
Meeting Compliance Standards in the US: HIPAA, SOC 2, NIST 800-53
Regulatory compliance isn’t optional—failing to secure APIs can lead to lawsuits, financial penalties, and reputation damage.
Checklist: Must-Have Security Measures for MuleSoft Deployments
| Data Encryption: Use SSL/TLS and encrypt sensitive data in transit and at rest. |
| Access Controls: Implement OAuth 2.0, JWT, and role-based access controls (RBAC). |
| API Security Policies: Enforce rate limiting, IP whitelisting, and authentication checks. |
| Audit Logging: Maintain detailed logs of API requests for security monitoring. |
| Automated Security Testing: Integrate static and dynamic security scans into CI/CD. |
Key Compliance Requirements for MuleSoft APIs
| Regulation | Key Security Requirements |
| HIPAA (Healthcare) | Protect patient data (PHI) with encryption and access controls. |
| SOC 2 (Cloud Security) | Maintain strict data access policies and conduct regular security audits. |
| NIST 800-53 (Government) | Implement multi-layered security and continuous monitoring of APIs. |
Non-compliance can result in:
- HIPAA fines of up to $1.5M per violation
- SOC 2 violations leading to business disruptions and lost customers
- Government contracts being revoked due to NIST 800-53 failures
Solution: Automated code scanning ensures continuous compliance by enforcing security best practices before deployment.
Final Thoughts: Why Code Scanning is a Must for MuleSoft CI/CD
- Vulnerabilities can cripple MuleSoft APIs, but automated code scanning prevents them before they reach production.
- Businesses that integrate scanning into CI/CD pipelines improve security, reduce costs, and stay compliant.
- Regulatory standards like HIPAA, SOC 2, and NIST 800-53 mandate strong security—automated scanning enforces these requirements effortlessly.
Setting Up CI/CD Pipelines for MuleSoft with Integrated Code Scanning
Integrating CI/CD pipelines with automated code scanning is crucial for ensuring secure, compliant, and high-quality MuleSoft applications. But how do you set up a pipeline that effectively scans your MuleSoft code without slowing down development?
This part walks through essential DevOps tools, version control strategies, and best practices for enterprise MuleSoft projects.
CI/CD Setup for MuleSoft: Essential Tools and DevOps Environments
To create an efficient CI/CD pipeline for MuleSoft, you need tools that support:
- Automated builds and deployments
- Seamless integration with code scanning tools
- Compliance enforcement and security checks
Pro Tip: MuleSoft integrates with all these tools, allowing teams to choose the best fit for their DevOps workflows.
How CI/CD and Code Scanning Fit into the MuleSoft Ecosystem

If issues are found? The pipeline blocks deployment, notifies developers, and suggests fixes.
This prevents security flaws from reaching production while maintaining fast, automated releases.
Version Control and Branching Strategies for Enterprise MuleSoft Projects
Managing version control and branching effectively is key to ensuring smooth deployments in large-scale MuleSoft environments.
Recommended Branching Strategy for MuleSoft CI/CD
Suggested Workflow:
- Main Branch (Master/Production): Contains only fully tested and approved code
- Develop Branch: Used for ongoing development before merging into production.
- Feature Branches: Developers create these for specific enhancements or bug fixes
- Release Branches: Used for stabilizing code before major releases.
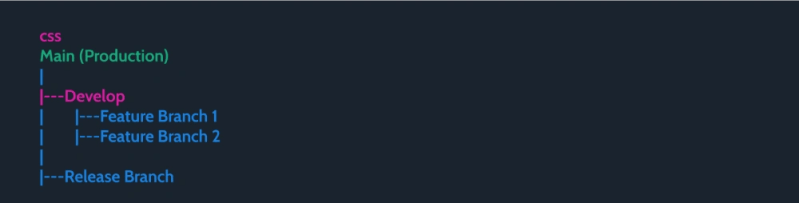
Pro Tip: Use merge requests (MRs) or pull requests (PRs) to ensure every branch is scanned before merging.

By following these strategies, enterprises can enhance security, streamline deployments, and maintain high code quality in MuleSoft projects.
Step-by-Step Guide: Integrating Code Scanning into MuleSoft CI/CD Pipelines
Integrating automated code scanning into MuleSoft CI/CD pipelines is essential for identifying vulnerabilities before deployment. This step-by-step guide walks you through the following:
- Setting up the development environment
- Configuring security tools like Falcon Scan
- Automating scanning triggers in CI/CD pipelines
- Setting up dashboards and alerts for monitoring
By following these steps, you’ll ensure secure, compliant, and high-quality MuleSoft applications. Let’s dive in!
Development Environment Setup for MuleSoft and Code Scanning Tools
Before integrating code scanning, you need a properly configured environment with:
Install and Set Up MuleSoft Development Environment
- Install Anypoint Studio (MuleSoft’s IDE)
- Set up Mule runtime for local testing
- Configure Git for version control
Install a Code Scanning Tool
Tools suggestion:
SonarQube – Static code analysis
Falcon Scan – All-In-One (Recommended)

Integrating Tools Like Falcon Scan with MuleSoft
Code scanning tools automatically analyze MuleSoft applications for security vulnerabilities, API misconfigurations, and compliance gaps.
Step-by-Step: Integrating Falcon Scan
Refer this: Falcon Suite Integration
Code Fixes After Security Scan
Before Scan:
| Insecure API exposed using HTTP protocol |
| <http:listener-config name=”HTTP_Listener_config” > <http:listener-connection host=”0.0.0.0″ port=”8081″ /> </http:listener-config> |
After Scan Fix:
| API exposed using HTTPS protocol |
| <http:listener-config name=”HTTP_Listener_config” > <http:listener-connection host=”0.0.0.0″ port=”8081″ protocol=”HTTPS”/> </http:listener-config> |
Result: All API requested will now be using secure HTTPS protocol for communication
Pipeline Automation: Trigger-Based Code Scanning and Continuous Testing
To ensure continuous security, code scanning should be automatically triggered in the CI/CD pipeline.

Must-Have Triggers for Code Scanning
- Pre-commit Hooks – Prevents insecure code from being pushed
- Pull Request Validation – Scans code before merging
- Scheduled Scans – Regular scans for security regressions
Example GitLab CI/CD configuration:
| security_scan: stage: scan script: – mvn falcon:scan allow_failure: false |
- This ensures that code scanning runs automatically before each build.
Setting Up Alerts, Dashboards, and Quality Reports in CI/CD Tools
Configuring Security Dashboards in Jenkins/GitLab
- Jenkins: Install SonarQube plugin
- GitLab: Enable Security & Compliance Center
Example: Security Dashboard Metrics
| Metric | Why It Matters | Threshold |
| API Vulnerabilities | Detects security flaws | Zero critical issues |
| OWASP Compliance | Ensures protection against common threats | 100% compliance |
| Code Quality Score | Identifies maintainability issues | 80% or higher |
Final Thoughts
By integrating code scanning into MuleSoft CI/CD pipelines, organizations can:
- Catch security flaws early
- Ensure compliance with regulations like HIPAA & SOC 2
- Deploy secure MuleSoft applications with confidence
Best Practices for Secure and Efficient Code Scanning in MuleSoft Pipelines
Integrating code scanning into your MuleSoft CI/CD pipeline is just the first step.
To make it effective and developer-friendly, you need to implement security gates, optimize performance, and ensure developer buy-in.
Here’s how you can do it.
Implementing Quality Gates, Scan Thresholds, and Reporting Metrics
Quality gates act as security checkpoints in your pipeline, stopping deployments if vulnerabilities exceed a set threshold.
Essential Security Gates for MuleSoft CI/CD
- Pre-commit scans – Catch vulnerabilities before code enters the repository
- Pull request security reviews – Enforce security scanning before merging
- Build-time scanning – Identify issues before deploying to production
- Post-deployment monitoring – Detect threats in live APIs
Recommended Thresholds for Security Risks

- Pro Tip: Regularly adjust thresholds based on compliance requirements like HIPAA, SOC 2, and NIST 800-53.
Reducing False Positives and Gaining Developer Buy-In for Code Scanning
Developers often resist security scans due to false positives and slow build times. Here’s how to tackle that.
Why Developers Resist Code Scanning & How to Fix It
Common Issues:
– Too many false positives
– Scanning slows down CI/CD
– Unclear security reports
Solutions:
– Fine-tune scanning rules – Adjust detection sensitivity to reduce noise
– Whitelist known safe code – Avoid flagging harmless code
– Use fast, incremental scans – Only scan new/modified code
– Provide actionable reports – Show exact fixes instead of generic warnings
Pro Tip: Work with developers to prioritize security fixes that impact production the most.
Maintaining Pipeline Security and Performance Optimization
Security shouldn’t come at the cost of pipeline performance. Follow these best practices to keep things secure and efficient.
CI/CD Security Best Practices vs. Common Mistakes
| Best Practice | Common Mistake |
| Use parallel scanning to speed up builds | Running full scans on every commit, slowing pipelines |
| Automate vulnerability triaging | Manually sorting through scan results |
| Secure CI/CD secrets & API keys | Hardcoding credentials in pipelines |
| Enable runtime security monitoring | Only relying on static scans |
Checklist: Actions to Optimize Pipeline Performance
- Use caching to speed up repeated scans
- Schedule full scans at off-peak hours
- Run security tests in parallel with functional tests
- Only scan changed code, not the entire codebase
Future-Proof Your MuleSoft CI/CD with Automated Code Scanning
The threat landscape is evolving, and MuleSoft developers must stay ahead by integrating automated security scanning into their CI/CD pipelines.
As organizations continue to adopt DevSecOps, security can no longer be an afterthought—it must be embedded into development workflows from the start.
Try Falcon Scan, with 230+ automated rules. It helps improve code quality, enhance security, and reduce development costs by up to 80%
What’s Next for Automated Security in MuleSoft CI/CD?
- AI-Driven Security Scanning – Falcon AI(Integrated with Falcon Scan) leverages machine learning to detect patterns, predict vulnerabilities, and proactively enhance MuleSoft security before threats emerge.
- Shift-Left Security at Scale – More enterprises will move security earlier in the SDLC, ensuring that developers fix vulnerabilities before code even reaches staging.
- Zero-Trust CI/CD Pipelines – Expect increased adoption of identity-based access controls to prevent unauthorized changes in automated deployments.
- Self-Healing Security Pipelines – Imagine CI/CD pipelines that automatically remediate vulnerabilities without human intervention!
Future DevSecOps Trends Impacting MuleSoft
- 90% of enterprises will adopt automated security scanning in CI/CD by 2026
- Cloud-native security tools will become standard in API development
- Compliance automation will streamline audits for regulations like HIPAA and SOC 2
FAQs – MuleSoft Code Scanning & CI/CD Pipeline Integration
1. What Are the Best Code Scanning Tools for MuleSoft Projects?
Falcon Scan is the best and only enterprise-ready solution for MuleSoft security, offering deep scanning, real-time threat detection, and seamless CI/CD integration. Unlike general tools like SonarQube or Checkmarx, Falcon Scan is built specifically for MuleSoft, minimizing false positives and maximizing security accuracy.
2. Can Falcon Scan Be Integrated into MuleSoft CI/CD Pipelines?
Yes! Falcon Scan seamlessly integrates with MuleSoft CI/CD tools like GitLab, Jenkins, and Azure DevOps.
3. How Does Falcon Scan Enhance Code Quality and Security in MuleSoft?
Before Falcon Scan: Critical security flaw in API authentication detected
After Falcon Scan: Issue fixed, API hardened against threats.
Falcon Scan provides actionable insights, helping developers fix vulnerabilities before deployment.
4. Is Code Scanning Mandatory for Enterprise MuleSoft Deployments?
Yes, many industry compliance standards require code scanning for security and regulatory adherence. Key standards that mandate code scanning include:
- HIPAA (Healthcare) – Ensures patient data protection and mandates security assessments.
- SOC 2 (Data Security) – Requires continuous monitoring and vulnerability scanning.
- NIST 800-53 – Enforces strict security controls for federal information systems.
- PCI-DSS (Payment Security) – Mandates secure coding practices to protect payment data.
For enterprises handling sensitive data, integrating automated code scanning into MuleSoft CI/CD pipelines is not optional—it’s essential for compliance and risk mitigation. ✅
5. How Frequently Should Code Scanning Be Run in CI/CD Pipelines?
The ideal scanning frequency depends on your project’s size and security requirements:
- Ad-hoc scanning – Suitable for small projects with occasional manual security checks.
- Per-commit scanning – Helps catch vulnerabilities early in the development process.
- Scheduled scanning (daily/weekly) – Ensures continuous security monitoring for enterprise environments.
6. Which US Compliance Standards Require Code Scanning in Integration Projects?
- HIPAA – Protects patient data in healthcare APIs
- SOC 2 – Ensures secure handling of customer data
- NIST 800-53 – Federal security compliance framework
- PCI-DSS – Mandatory for payment processing security







